Table of Contents
Did you know that about 70% of businesses worldwide choose to lease assets rather than buy them outright? Not just that, knowing the different leases types can help individuals and companies handle their finances better.
No one talks about the question, "If leasing is so common, why do many people still mix it up with renting?" That is why you need to know about the various leases.
Simply put, a lease is an agreement in which the owner allows another person or business to use an asset for a set time and pays regularly in return. Now, let’s look at how leases work and differ from renting in daily life.
What is Leases?
A lease is a written legal agreement between the lessor (owner) and the lessee (borrower). It permitted the lessee to use an asset for a fixed duration in exchange for regular payments, like rent.
- The lessee uses an asset, such as a car, property or tool, for a particular duration rather than purchasing it outright. Leasing helps save money by avoiding an upfront cost.
- Commercial leases are agreements to rent business assets such as office spaces, warehouses, retail stores or industrial facilities.
- It offers flexibility with fixed monthly payments, can give you tax benefits since payments are often deductible.
- It allows borrowers to buy expensive assets without needing a large investment corpus.
Keep in Mind: Real estate mainly works through two leases: commercial and home rental agreements.
Before investing through leasing, let us know the types of leases.
Types of Leases
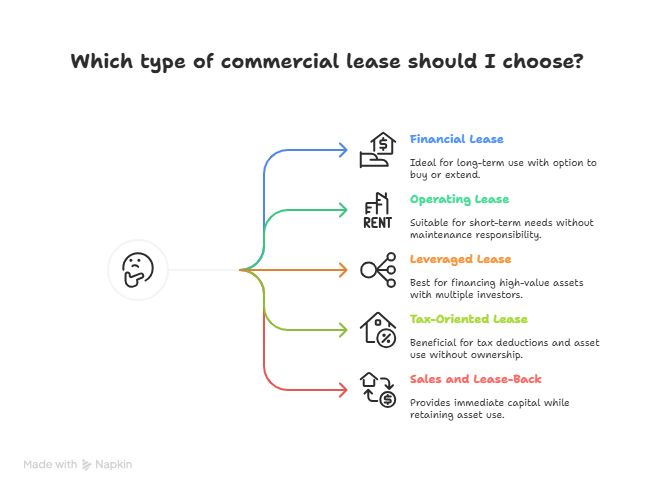
Here are the commercial lease types you should know about:
-
Financial Lease
- In this, the lessor owns the asset, but the borrower (you) gets to control it for the lease term. Ultimately, you can buy, return or extend the lease.
- Example:A construction company leases heavy machinery like bulldozers or cranes for several years. The company uses the machines & after the lease term, it may decide to buy or return them.
- It is perfect for businesses that require expensive equipment without the full upfront cost, but with long-term use benefits.
- It is often used in sectors like logistics, manufacturing or construction.
-
Operating Lease
- An operating lease is a short-term lease in which the asset is returned to the owner after the contract term has expired. You do not own the asset, the owner covers all the maintenance and services.
- Example: A retail chain leases its delivery trucks for a short term. After the lease ends, the trucks are returned to the lessor, and the retail chain either rents them again or gets new vehicles.
- It is mainly used in companies that need assets temporarily or don’t want the hassle of maintaining them, such as for office equipment, vehicles, or short-term tech.
-
Leveraged Lease
- This lease involves multiple investors who contribute to financing a high-value asset. The lessor arranges financing with outside investors or a bank, and the asset is leased out.
- Example: Suppose an airline wants to lease a jet but lacks the full capital. They use a leveraged lease, in which multiple investors, including a bank, contribute to the cost of the airplane. To operate the jet and get a portion of the lease rental income on behalf of investors.
- Typically used for expensive assets like airplanes, ships or large industrial machinery.
- It is a way for multiple parties to share the cost of acquiring an asset.
-
Tax-Oriented Lease
- This lease allows the borrower to use an asset in exchange for a monthly fee. At the end of the lease period, the asset is returned to the lessor. It is also called a "true lease" as the lessor receives the tax benefits.
- For instance, a tech company leases servers for its data centre operations. The company pays a monthly fee to use the servers but does not purchase them. After a specific period, the company returns them to the lessor.
- This tax-oriented lease benefits the lessor by providing tax deductions while allowing the lessee to use the asset without the hassle of ownership.
- It is commonly used for IT equipment, vehicles or machinery.
Start Your SIP TodayLet your money work for you with the best SIP plans.
-
Sales and Lease-Back
- A company sells an asset, often real estate or equipment, to an investor in exchange for urgent cash and then immediately leases it back to continue using it.
- For instance, a manufacturing company sells its factory to an investor but leases it back to continue operations without owning the building.
- This provides the company with capital while allowing it to use the asset.
- Businesses often use this strategy to raise capital quickly without losing access to essential assets. Investors profit from continuous rental income and the company gains cash flow for expansion or other requirements.
- Let us break down how a lease actually functions from start to finish.
Pro Tip: Use a Tax Calculator to estimate your income tax liability.
How Does a Lease Work?
Here is how a lease generally works:
- Contract Terms: The lessor (owner) and lessee (renter) contract is based on terms such as lease duration, rental amount & payment date.
- Asset Use: The lessee gets the right to use the asset, such as vehicles or property, for a particular time as agreed in the agreement.
- Duties:The lease comes with duties like maintenance, insurance and taxes based on the lease type.
- Payment: The lessee makes asset payments to the owner monthly, quarterly, etc.
- End of Lease: At the end of the lease phase, the borrower can return the asset, renew it, or purchase an item.
- Legal Rights: The lease agreement papers help both parties by providing transparent, clear terms, policy of asset uses, payment duties and penalties for non-compliance.
Moving to the next important headline, bursting the Bubble of Doubt: Lease vs Rent.
Smart Investments, Bigger Returns
Lease vs Rent: What's the difference?
The table below highlighting the difference between lease and rent:
| Factor | Lease | Rent |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Long-term (months to years) | Short-term (generally month-to-month) |
| Commitment | Fixed commitment for the entire term | Flexible, can change every month |
| Ownership | No ownership, you control the asset for the term | No ownership, just pay for temporary use |
| Payment | Fixed payments for the whole lease term | Payments are usually month-to-month |
| Responsibilities | Lessee may handle maintenance and repairs | Landlord typically handles maintenance |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, fixed terms and conditions | More flexible, can end or change anytime |
| Common Use | For long-term business assets (e.g., equipment, real estate) | For short-term housing or temporary use |
| Option to Buy | May have an option to purchase at the end | No option to buy, simply rent the space |
Conclusion
To wrap up this blog, exploring the different types of leases can help you "make your money work for you." Each type of lease offers benefits, either for a short-term operating lease or a long-term financial lease.
However, if you know how leases differ from renting, you can choose a lease that helps you manage assets and costs more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Can I buy the asset at the end of a lease?
Yes, in finance and capital leases, you can buy the asset at the end of the lease period.
-
What are the tax benefits of leasing?
Leasing can offer tax benefits, especially for the lessor, who can claim deductions. This makes leasing attractive for businesses wanting to lower their taxable income.
-
Why would a business choose a lease over buying an asset?
Leasing helps businesses avoid large upfront costs, keeping their cash flow continue. It also offers flexibility, such as the option to return the asset after the lease term.
-
Is leasing better than financing a purchase?
Leasing works best if you need flexibility & lower upfront costs. Financing a purchase is better if you want long-term ownership and the asset’s potential increase in value.
-
What are the main advantages of a finance lease?
With a finance lease, you get long-term access to an asset, potential tax benefits and the option to buy it later, making it ideal for expensive equipment.
-
Can a lease agreement be modified?
Yes, lease terms like duration, rent or asset details can be adjusted if the lessor and lessee agree.




.png&w=3840&q=75)






_(1).webp&w=3840&q=75)


