Table of Contents
- What is a Recession?
- What Causes a Recession: Factors and Their Examples
- Is India Heading Toward a Recession in 2026?
- Can India Avoid a Recession in 2026?
- Complete History of India Facing Recessions
- What are the Main Indian Economic Indicators for 2026
- Impact of a Recession on the Indian Economy and Markets
- Most Affected Sectors of India During a Recession
- RBI, Central Bank and Government Responses in Recessions
- How can Common People, Businesses and Investors Prepare for a Recession?
- Recession Proof Stocks in India for 2026
- Conclusion
Every few years, the word "Recession" appears in the headlines and makes everyone worried. In 2026 also with US tariff talks, oil price changes and global trade concerns growing, everyone's asking: Is there a possibility of a recession in India in 2026 or will our economy keep growing?
Well, the 2026 GDP growth estimation of 6.5%-7.5% and other factors only scream growth and there are no traces of a recession in India. In fact, India is expected to be the fastest growing major economy in the world in 2026. However, there are still some external risks to consider.
Read this post to find out why 2026 is likely to be a year of growth for India and the chances of a recession are low. Also, know which are the safe sectors to watch and smart strategies to prepare your portfolio.
Buy Digital Gold Online Safely and Start Your Gold Journey at Just ₹100 now

What is a Recession?
A major and lasting decline in economic activities across an economy can be defined as a recession, which usually lasts more than a few months.
There is no single official definition of a recession, it can differ for every economy. For instance, in the US, the NBER (National Bureau of Economic Research) is responsible for declaring a situation a recession based on various indicators like GDP.
However, in India, a recession is described as two consecutive quarters of downturn in the real GDP of the country. This is the definition, economists and some countries (UK, EU and Canada) often use.
A recession also brings a decline in other factors like industrial production, sales, employment and income. This makes recessions distinct from short-term slowdowns or depressions, which are far deeper and longer-lasting.
Now that it is clear what a recession is. Let us understand what causes one.
What Causes a Recession: Factors and Their Examples
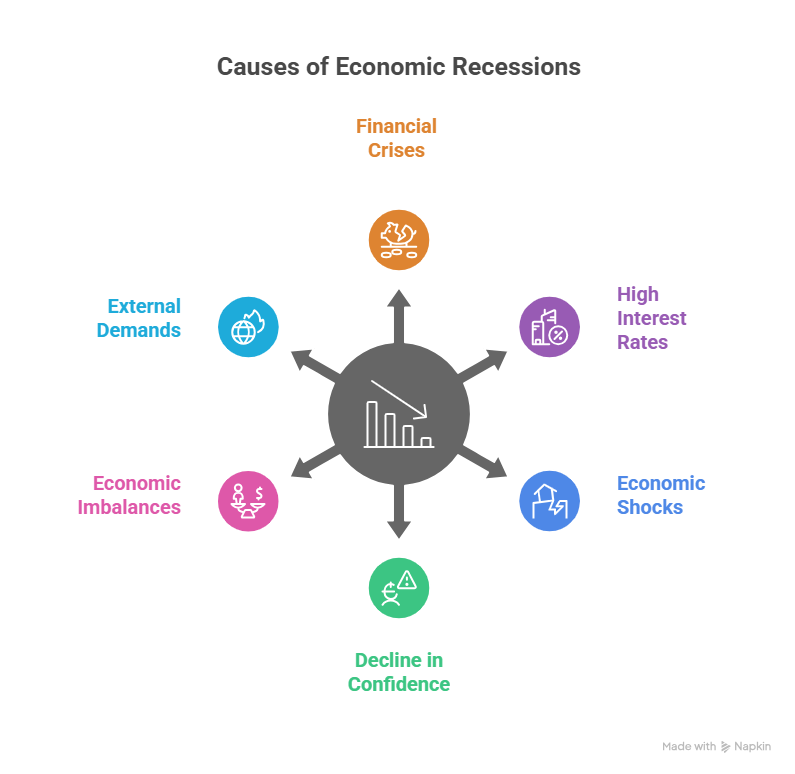
Recessions occur when a mix of economic, financial and psychological factors causes a significant drop in spending and economic activity of a country. However, there is no single cause of a recession. There are many factors that can cause a downturn in the country's economy, including:
-
Financial Crises & Asset Bubbles
When asset bubbles burst, they can cause a financial crisis. This often happens after too much credit is given or debt is taken on. A clear example of this is the 2008 Global Financial Crisis, which started with the subprime mortgage crisis.
-
High Interest Rates and Monetary Policy
While fighting high inflation, if the central banks raise the interest rates too quickly or too high, it can make borrowing more expensive for businesses & consumers, which can slow down the economy enough to cause a recession, known as a hard landing.
-
Economic Shocks
Sudden and unexpected events can disrupt the economy of a country, including its supply chains, production and trade, which leads to higher costs and lower output. The examples include the 1970s oil embargoes & the COVID-19 pandemic recession in 2020.
-
Decline in Consumer & Business Confidence
When people and businesses are worried about the economy, they tend to save more money and cut back on their spending and investment. This cut off can create a negative cycle that makes the economy worse or even leads to a downturn.
-
Economic Imbalances
When there are differences like between production and consumption, income inequality or too much capacity in specific industries, the economy can become weak, leading to an economic downturn when it becomes too much to handle.
-
External Demands
Countries that rely on selling goods can go into a recession if their main trading partners buy less or stop buying. This is because the world economy is connected.
Now, let us jump to the main question: Is a Recession Coming in India in 2026? Keep reading to know.
Must Read: Recession vs Depression – The Economic Difference That Matters
Best Mutual Funds for 2026 Backed by Expert Research

Is India Heading Toward a Recession in 2026?
No, India is not suppose to enter in a recession in 2026, as there are no signs of one occurring. In fact, it is expected to be one of the fastest-growing major economies in the world this year.
Several major economic organizations predict that India will grow strongly in the 2026 financial year. Here are some of their predictions:
- National Statistics Office (Government of India): 4% growth projection.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI): Revised forecast of 3% growth.
- International Monetary Fund (IMF): 6% growth projection.
- World Bank: 5% growth forecast.
- United Nations: 6% growth projection.
With the estimations of the above mentioned institutions, India is expected to show strong GDP growth of 6.5% to 7.5% because of strong domestic demand, increased public investment and support from government policies. Low inflation, around 2-4% and rate cuts by the RBI will also help in maintaining stability. Other positive factors include strong monsoons, lower crude oil prices ($65-70 per barrel) and government infrastructure spending, which help maintain a low current account deficit (around 1% of GDP).
However, global risks still exist with downside threats like US tariffs, trade uncertainties and weaker exports. If these issues worsen, they could reduce growth by 0.5%. A US recession, which JPMorgan estimates has a 35% chance of happening, could pressure India by slowing global demand.
Overall, the chances of a recession are low in India. There are no signs of a decline, like a two-quarter drop in GDP and growth predictions are also positive. The economy has managed challenging situations before. But, staying alert because if global risks increase or changes in our country slow down, a downturn could occur.
Moving on, let us know if India is capable of handling a recession or not, if it happens.
Can India Avoid a Recession in 2026?
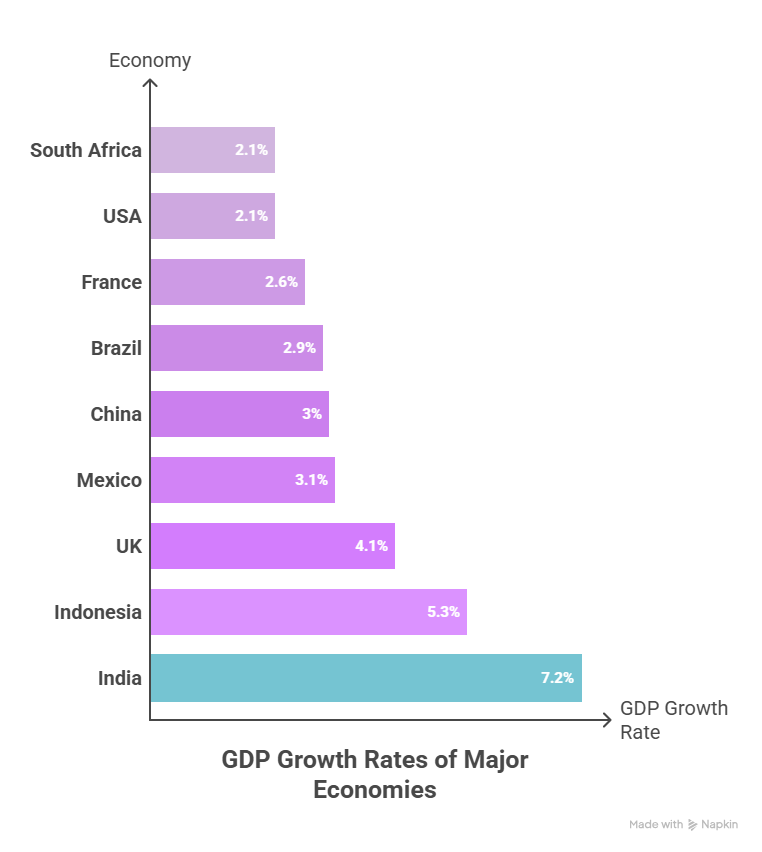
According to the current economic data and estimations from major institutions, India can avoid a recession in 2026 if one occurs and recover quickly. India is expected to be the fastest-growing major economy in the world. Strong domestic factors can help it manage potential global economic slowdowns and external risks.
India's growth is supported by a GDP growth forecast of 6.5% to 7.5%. Strong domestic demand, a supportive monetary policy and healthy foreign exchange reserves contribute to this positive outlook.
However, economists also see some challenges ahead. These challenges include possible recessions in other major economies, the impact of US tariffs, ongoing global trade uncertainties and concerns about inflation.
You must be wondering whether India has faced Recessions before. Let us know in the next part.
Complete History of India Facing Recessions
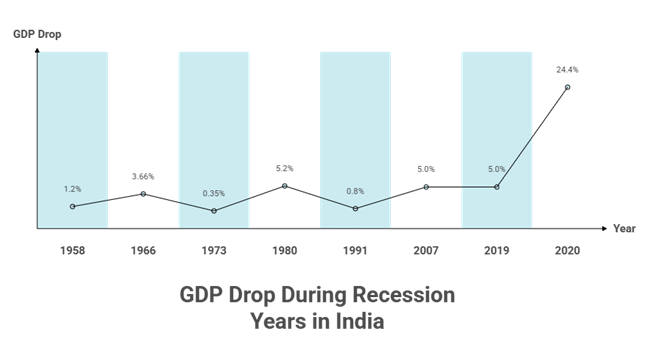
Throughout its history, India has faced a recession multiple times since gaining independence. The following are the recessions that occurred in India:
-
1957-1958 BOP Crisis
It was the first recession in India after gaining independence. It was caused due to severe drought and a balance of payments crisis, which caused a 1.2% drop in GDP nationwide.
-
1965-1966 Severe Drought
After wars with China and Pakistan, the country faced two serious droughts, causing the economy to shrink by 3.66%.
-
1973 Oil Shock
The oil embargo by OAPEC caused a sharp rise in oil prices by 400%, which led to high inflation and a decrease in GDP by 0.35%.
-
1980 Another Oil Shock
It was caused by the Iranian revolution and the Iran-Iraq war, which led to a serious balance of payments problem and a GDP decline of 5.2%.
-
1991 Balance of Payment Crisis
Due to the Gulf War and high levels of debt, the reserves were drained, and only three weeks’ worth of imports were left; GDP fell 0.8%. So, India pledged gold to get IMF support and liberalized.
-
2007 Global Financial Crisis
After Lehman Brothers collapsed, foreign investments dropped in India and GDP fell to 5.0%. The banks and government support helped prevent a deep recession and limited the damage.
-
2019 Economic Slowdown
During this time, the GDP of India fell to 5%. Weak demands, slow manufacturing and struggling banks caused the economic downturn.
-
2020 COVID-19 Pandemic
This was the first technical recession of India since it began tracking quarterly GDP data in 1996. The lockdown stopped industries and the GDP collapsed by 24.4%.
In the next section, let us see what the key economic indicators are that you should watch in 2026.
Start Your SIP TodayLet your money work for you with the best SIP plans.
What are the Main Indian Economic Indicators for 2026?
The following are the primary economic indicators and projections for India in 2026:
1. Growth and Output
| Indicator | FY2026 Projection | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Real GDP Growth | 7.4% | Up from 6.5% in FY25; services lead at 9.1% |
| Nominal GDP Growth | 8.0% | Reflects price stability gains |
| Manufacturing Growth | 7.0% | Strong alongside construction at 7.0% |
| Real GVA Growth | 7.3% | Broad-based sectoral pickup |
2. Inflation and Monetary Policy
| Indicator | FY2026 Projection | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| CPI Inflation | ~2.0% | Nov 2025 at 0.71% YoY; benign trend |
| WPI Inflation | Deflationary | Cooling producer prices in H2 2025 |
| RBI Repo Rate | 5.25% | Multiple cuts since Feb 2025 for growth support |
3. Financial and External Sector
| Indicator | FY2026 Projection | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fiscal Deficit | 4.4% of GDP | Ongoing consolidation path |
| Trade Deficit | Widened | Imports outpace exports; services exports buffer |
| Forex Reserves | ~$702.8B | As of June 2025; strong external shield |
4. Consumption and Investment
| Indicator | FY2026 Projection | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Private Consumption (PFCE) | 7.0% | Boosted by tax relief, low rates |
| Govt Consumption | 5.2% | Higher public spending vs prior year |
| Gross Fixed Capital Formation | 7.8% | Robust investment momentum |
Must Read: Richest State in India 2025 | Updated GDP Ranking by Experts
If a recession occurs, how will it impact the economy of our country? Let us know next.
Impact of a Recession on the Indian Economy and Markets
Here is the description of the impact a recession can have on the Indian economy and stock market:
Impact on the Indian Economy
- The most direct impact is a decline in GDP for two consecutive quarters.
- Financial difficulties for businesses lead to unemployment.
- Consumer spending reduces due to job losses and income reduction.
- Reduced demand and tighter credit conditions lead to business failures.
- As global demand falls, India's export-oriented sectors face a decline.
- Tax revenues decrease and government spending increases, resulting in a wider financial difference.
- Banks face more loan defaults and Non-Performing Assets (NPAs), leading to a credit crunch in the domestic market.
Impact on Indian Markets (Sensex & Nifty)
- Stock markets can experience a big drop, which can make investors feel negative.
- International investors can pull back their money and this foreign investment outflow can pressure stock prices.
- When demand decreases, companies still face the same operational costs. This situation can cause their share prices to drop.
- Different sectors react differently to changes in the market. Industries that focus on exports, like manufacturing, real estate and hospitality, are often hit the hardest.
- Short-term mutual fund investments can also take a hit due to a decline in the stock market.
Now, let us look at the most affected sectors of India in a recession.
Most Affected Sectors of India During a Recession
During a recession, the cyclical sectors suffer the most in India during a recession due to decreased demand, exports and credit drops of 30-60% (seen in 2008/2020). Look at the table below for a specific list:
| Sector | Why Vulnerable | Past Drops | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metals | Global demand crash, commodity prices tank | -50%+ (2025 tariff route) | Tata Steel, JSW Steel |
| IT / Services | US/EU client cuts, FII outflows | -38% (2020) | Infosys, TCS |
| Autos | Consumer spending freeze, high rates | -40% (2019 slowdown) | Tata Motors, Maruti |
| Realty | Loans dry up, no home buys | -60% (2008) | DLF, Godrej Properties |
| Banks / NBFCs | NPAs rise, lending halts | -30% (2020) | ICICI Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank |
Moving on, let us learn how the government bodies react during a recession.
RBI, Central Bank and Government Responses in Recessions
The following are the responses of these entities during a recession in India:
Reserve Bank of India (Monetary Policy)
- Lower key policy interest rates, like the repo rate.
- Supports liquidity infusion by reducing the needs of CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio) and SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio).
- Conducts OMOs (Open Market Operations).
- Providing special liquidity facilities to specific stressed sectors.
- RBI provides temporary relief from regulatory measures.
- Support the Indian rupee and manage the country's foreign currency reserves.
Government of India (Fiscal Policy)
- The government increases its spending on infrastructure and public welfare programs.
- The government announces economic help that includes both immediate support and long-term changes.
- Provides support to highly affected sectors through incentive schemes.
- The Central government may temporarily raise the borrowing limits for state governments to manage their finances.
Key Central Bank Responses
- The most common and immediate response is the reduction of benchmark interest rates.
- If interest rates are already near zero and further cuts are not possible, central banks use unusual measures like QE (Quantitative Easing).
- Central banks do OMO and buy or sell government securities to influence the money supply.
- These banks can reduce the reserve requirements for commercial banks.
- In difficult financial times, it lends emergency money to banks that need help.
- It uses public statements and communicates about its future policy intentions to manage market expectations.
- In some cases, central banks may intervene in foreign exchange markets to stabilize their national currency.
Important Read: Top 10 GDP Countries 2025: World GDP Rankings 2025
Next, let us know how you should prepare yourself if a recession occurs in India.
How can Common People, Businesses and Investors Prepare for a Recession?
Getting ready for a recession means using smart financial strategies to strengthen your finances and reduce risks for individuals, businesses and investors. Here is how to prepare:
For Common People (Households)
- Commoners should build an emergency fund & save 3-6 months' worth of their living expenses.
- Pay off all your debts, especially the high-interest ones, to save more.
- Consider doing a side business or freelance work to create more income sources.
- Cut off the non-essential spending & prioritize your basic needs only.
- Review your investments, like mutual fundsor SIPs and match your portfolio with your risk tolerance and horizon.
For Businesses
- Identify essential business operations and cut non-essential costs.
- Improve the cash flow management of your company.
- Establish a good relationship with your bank before a recession hits.
- Do not depend on a few clients & diversify your customer base.
- Make use of technology to automate operations, improve efficiency & reduce labour costs in the long run.
For Investors
- Diversify your investment portfolio & invest in various sectors and asset classes.
- Focus on companies with high-quality stocks that are well-established.
- Investing through SIPlowers your average costs and smooths market ups and downs.
- Increase your allocations to defensive assets like government bonds.
- Do not invest in mutual funds or other investment vehicles with borrowed money.
- Avoid panic selling & focus on your long-term investment goals.
- Diversify your portfolio in gold investments like Gold Mutual Funds and Gold ETFs.
Pro Tip: Use a SIP Calculator and estimate the future returns of your SIP investment easily.
After knowing the safety measures to take during a recession, let us know some stocks and sectors that would not be affected even if India faced a recession in 2026.
Recession Proof Stocks in India for 2026
The following are the stocks and sectors that are safe to invest in India during a recession in 2026:
| Sector | Why Resilient | Top Stocks |
|---|---|---|
| FMCG | Essentials like soap, food—people never skip | HUL, Nestle India, ITC, Britannia |
| Healthcare / Pharma | Meds & hospitals: Health doesn't wait | Sun Pharma, Divi's Labs, Dr Reddy's, Cipla, Lupin, Apollo Hospitals |
| Utilities / Energy | Power, fuel: Bills keep coming | Coal India, ONGC, Torrent Power, Power Grid |
| Defence | Govt contracts, Atmanirbhar push—steady orders | BEL, HAL, Bharat Dynamics |
| Select Financials / PSUs | Strong balance sheets, govt backing | ICICI Bank, Kotak, SBI, IRCTC |
Conclusion
To conclude, India is entering 2026 with strong economic growth & very low chances of a recession. This growth is due to the increasing demand within the country, effective government policies, high GDP growth predictions and RBI policies.
Even though India faces some challenges from international means like US tariffs and trading uncertainties, its economic fundamentals are strong enough to overcome them and continue growing. Overall, India’s outlook for 2026 shows it will likely be the fastest-growing economy in the world.
Related Blogs:
- 2026 Finance Goals: 5 Key Personal Finance Rules for Better Money Management
- Smart SIP Strategy to Build a ₹2 Crore Wealth in 2026
FAQs
-
When will the India recession end if it starts?
Typically, recoveries take 6 to 18 months. For example, in 2020, the recovery happened in just 2 quarters due to stimulus.
-
What's worse: recession or inflation for Indians?
During a recession, job loss happens first, leading to unemployment rates over 8% and inflation quietly reduces savings.
-
Will the 2026 recession tank my mutual fund SIPs?
No, rupee cost averaging is effective. Buy more units at low prices to recover your investment, only pause if you face a cash emergency.
-
Role of gold in India's recession protection?
Gold is a strong investment, often increasing by 15-20% during market downturns (like the rally in 2020).
-
How does the monsoon affect India's recession risk?
Heavy rains have increased food prices by 2-3%, which affects rural spending since they account for 30% of consumption.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog is for educational purposes only and does not constitute professional, financial or investment advice. Economic and market forecasts are subject to change based on global events. Readers should consult with a qualified financial advisor before taking action.












