Table of Contents
Ever looked at your bank statement and wondered why your home loan payment suddenly increased or why the fixed deposit rates are not rising or maybe your SIPs in debt funds are acting strangely after the latest RBI announcement? Well, all your dilemma is because of RBI's dynamic duo: Bank Rate vs Repo Rate.
They are not just regular policy details because they can significantly impact your long-term borrowing costs, short-term cash flow, inflation and your following EMI change. Currently, the repo rate sits at 6.50% and the bank rate at 6.75%, shaping everything from EMIs to market moods in 2025.
In this post, you will explore the main differences between Bank Rate vs Repo Rate, look at trends from 2021-2025 and discuss why savvy investors track these rates to better time fixed deposits, loans and mutual funds. So, let us dive in.
What is Bank Rate?
The bank rate is the interest rate at which the RBI lends funds to commercial banks for a long time. The loans do not involve any collateral security.
This Rate directly impacts long-term borrowing costs, fixed deposit rates, and the overall cost of funds for banks. When the bank rate increases, the loans become expensive. When the RBI reduces the rates, then banks can borrow at a cheaper rate and may reduce lending rates. The Bank Rate is often influenced by long-term economic policies and not by daily liquidity needs. Below are the major functions of the bank rate: -
Controls Long-Term Credit Cost
A higher bank rate makes long-term borrowing expensive. A lower bank rate helps banks reduce interest rates for customers.
Shapes Long-Term Economic Policy
It supports RBI's decisions about long-term growth, inflation, & financial stability.
Impacts Fixed Deposit and Saving Rates
Since it affects the overall cost of funds, banks adjust FD rates based on the bank rate movement.
Encourages or Restricts Borrowing
If the RBI wants to reduce the money supply, it increases the bank rate. If it wants to support growth, it reduces the bank rate.
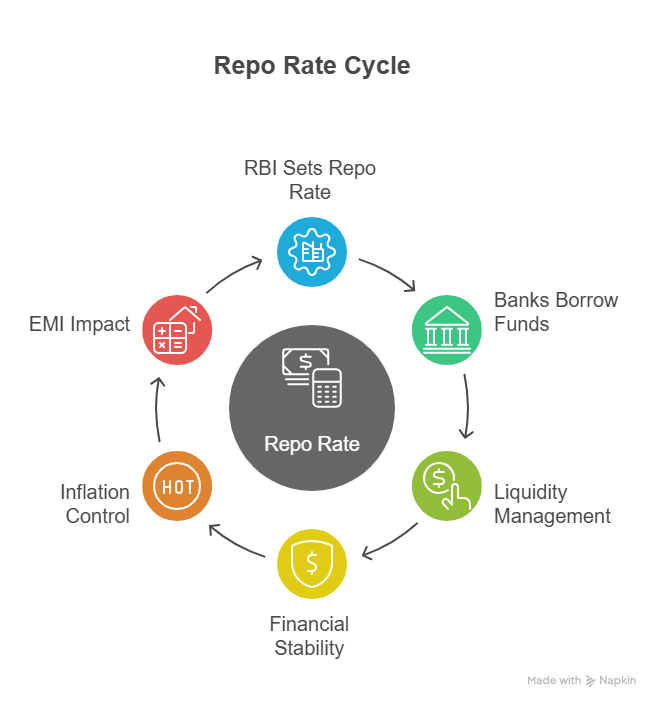
What is Repo Rate?
The Repo Rate is the interest rate at which the RBI provides lenders with short-term funds against government securities (collateral).
The funds are used by the bank to meet short-term requirements, especially when banks face temporary cash shortages. A higher repo rate results in expensive short-term borrowing, thus increasing EMIs. A lower repo rate reduces the overall interest rate in the economy. Let’s have a look at the major functions of repo rate: -
Maintains Short-Term Liquidity in Banks
Banks borrow from the RBI using government securities. This helps them manage short-term cash requirements.
Stabilises the Financial System
By adjusting the repo rate, the RBI keeps liquidity stable. This prevents shortages of funds in the banking system.
Controls Inflation
When inflation increases, the RBI raises the repo rate to control the excess flow of money. The RBI might cut the repo rate to increase consumer spending when inflation drops.
Directly Impacts EMIs and Loan Rates
Home loans, car loans, and business loans are linked to the repo rate. A small change immediately influences EMIs.
Did you know? : Did you know that a quick scan using a Mutual Fund Screener can predict how your debt funds might behave after a rate cut?
Both rates together help RBI maintain a balance between growth, inflation, liquidity and stability. Understanding the functions of the bank rate and repo rate helps every smart investor make better decisions in their financial planning.
Start Your SIP TodayLet your money work for you with the best SIP plans.
Difference between Bank Rate & Repo Rate
Understanding the difference between the bank rate and the repo rate helps investors track how the RBI controls liquidity, loan interest rates, EMIs, inflation and economic growth.
Below is a simple, updated and professional explanation.
The investors use the bank rate and repo rate as a major tool to track the economic mood of the country. These rates help RBI to control liquidity, loan interest rates, EMIs, inflation and monetary flow.
Quick Comparison Table: Repo Rate vs Bank Rate
| Feature | Bank Rate | Repo Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Long-term lending rate from RBI to banks | Short-term lending rate from RBI to banks |
| Collateral | No collateral | Needs government securities |
| Impact Period | Long-term | Short-term |
| Effect on EMIs | Indirect | Direct and immediate |
| Used For | Long-term credit management | Short-term liquidity and inflation control |
| Current Rate (2025) | 6.75% | 6.50% |
| Change Frequency | Low | High (MPC meets every 2 months) |
| Economic Influence | Structure and cost of long-term funds | Inflation, liquidity and short-term borrowing |
Latest Policy Rates (2025)
| RBI Interest Rate | % Value (2025) |
|---|---|
| Repo Rate | 6.50% |
| Bank Rate | 6.75% |
*The bank rate is generally set above the repo rate.
Bank Rate vs Repo Rate Trend (2021–2025)
| Rate (%) | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repo Rate | 4.00 | 4.40 | 6.50 | 6.50 | 6.50 |
| Bank Rate | 4.25 | 4.65 | 6.75 | 6.75 | 6.75 |
Must Read: RBI Repo Rate Cut 2025: Impact on Loans, Deposits & Markets
Why Should You Care About the Rates as an Investor or Borrower?
Understanding the bank rate and repo rate is not just for economists. These rates directly affect your SIPs, Debt Funds and overall financial planning. Know why every smart investor and borrower must analyse them precisely.
These Rates Determine Your EMI
Since 2019, the majority of floating-rate loans in India have been tied to the RBI Repo Rate. The EMI amounts for home loans, car loans and personal loans directly affect the changes in the repo rate.
Your FD and Debt Fund Returns Are Affected by These Rates
When the bank rate increases, it signals higher long-term borrowing costs, which could lead banks to raise Fixed Deposit (FD) rates. Debt mutual funds, corporate bonds and gilt funds tend to respond quickly to changes in policy rates. Understanding these shifts can also help investors identify the Best mutual funds to invest in under changing interest-rate conditions.
These Rates Influence Stock Market Trends
When the repo and bank rates rise, the market pays higher borrowing expenses, which can shrink its profit margins. On the other hand, when interest rates are reduced, loans become more affordable, making it easier for businesses to grow.
Your SIPs & Long-Term Portfolio Are Affected by Rates
Rate changes impact even equity SIP investors. A lower repo rate reduces borrowing costs, increasing corporate earnings and supporting market growth. Conversely, a higher repo rate slows loan growth, weakens economic activity and leads to more cautious market behaviour.
These Rates control the Indian Economy.
A stable repo rate with low inflation indicates controlled economic growth, healthy demand & a stable lending environment, creating an ideal scenario for investors, borrowers and businesses.
These Rates Affect Rupee Strength & Foreign Investment
Higher interest rates can attract foreign capital, making the rupee strong. Lower rates may spur domestic growth, but could reduce foreign portfolio investments (FPI).
These Rates Help You Time Loans, FDs, and Investments Wisely
These rates help you make smarter financial decisions.
Planning a home loan - keep an eye on the repo rate.
FD planning: watch the bank rate.
Debt fund investments: track expected rate cuts or hikes.
Long-term SIP wealth building: follow how rate cycles influence corporate earnings.
Smart Investments, Bigger Returns
Conclusion
In short, Bank Rate and Repo Rate are important tools the RBI uses to manage the economy. A change in the Repo Rate can quickly increase your EMIs, while the Bank Rate can influence long-term fixed deposit rates. These rates affect many things you care about, including your loans, SIPs, debt funds and even stock market trends.
Related Blogs:
- Old vs New Tax Regime 2025: Key Differences & Best Choice
- Top 10 Mutual Funds for SIP in 2025: Best Picks to Grow Wealth
Investors Also Ask
-
What is the main difference between the Bank Rate and the Repo Rate?
Bank Rate is for long-term lending by the RBI, while Repo Rate is for short-term borrowing by banks. -
Why does the Repo Rate affect EMIs directly?
Repo Rate affects short-term loan pricing, so banks revise home loan and personal loan EMIs immediately. -
What is the impact of the repo rate vs the bank interest rate comparison on borrowers?
Repo rate changes directly change interest rates on floating loans, affecting EMIs instantly. -
Do both rates affect mutual funds?
Yes. Repo rate changes affect debt fund returns quickly. Bank rate affects long-term bond yields. -
Why should borrowers track the repo rate & the bank rate?
Because these rates decide the cost of loans, EMIs, top-up loans, and refinancing opportunities. -
Are both rates important for SIP investors?
Yes. Rate cycles influence market trends, corporate earnings, and debt fund performance.




.webp&w=3840&q=75)



.webp&w=3840&q=75)




