Table of Contents
Investing in the financial market without knowing the role and functions of SEBI is like driving without traffic rules. It might work, but it is risky. The SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) is the traffic authority or rather, say financial market regulator in India, that takes care that the financial market works smoothly. The authority came into existence in 1988 but got its statutory powers in 1992.
But here is the part that usually surprises people: before SEBI came into existence in 1988, India did not have a proper regulatory body for its stock markets. This often led to fraud, scams and huge losses for investors. Today, SEBI not only protects the investors but also promotes transparency and fair trading practices.
Curious to know exactly how SEBI protects your money and keeps the market honest? Dive into this post to learn everything about this regulator and its powers. Keep reading as this could completely change the way you invest!
What is SEBI in the Indian Financial Market?
SEBI is the short form of the Securities & exchange Board of India. It is India's primary regulator for the securities market and the central authority that regulates the economic sectors in India. Before SEBI, the Indian markets were unsafe and poorly organized, leading to fraud and scams. Then the government realized that to attract domestic and global investment in India, a dedicated and independent authority was needed.
At the core, the role of SEBI is to protect the interests of investors while ensuring that the market functions reasonably and efficiently. It regulates stock exchanges, financial institutions and other market participants. This means everyone must follow the rules set by SEBI while buying, selling or managing securities in the market.
Now, let us see what the roles and functions of SEBI are.
Role of SEBI in the Indian Financial Market
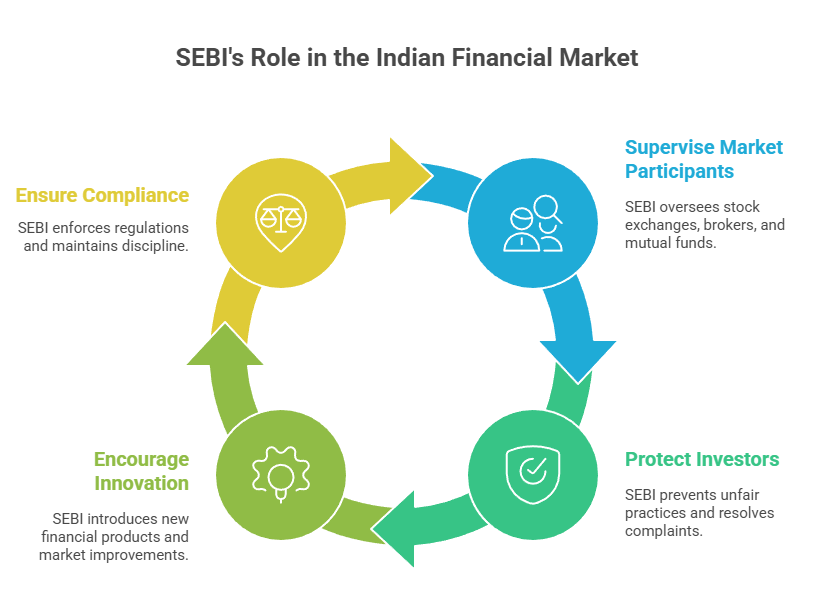
The role of SEBI goes beyond just regulations, ensuring that capital markets follow fair practices in an investor-friendly manner. It acts as a regulator, guardian and developer to strengthen the Indian capital market. Its key roles include:
- SEBI supervises stock exchanges, brokers, Mutual Funds and other intermediaries to maintain a smooth and orderly market operation.
- It protects investorsby stopping unfair practices and providing ways to resolve complaints.
- Apart from regulating the market, SEBI encourages innovation by introducing new financial products and improvements in market infrastructure to support long term growth.
- It ensures that all market participants follow regulations and maintain discipline across all financial sectors and securities.
Must Read: Tax on Mutual Funds: Complete Guide with Smart Saving Plans
Next, let us understand the functions of SEBI in Indian markets.
What is the Function of SEBI in Indian Markets?
While the key function of SEBI is to ensure that India's capital markets are safe and transparent, they are also innovative and modernized. These functions can be broadly categorized into protective, regulatory and developmental functions:
1. Protective functions
These functions focus on maintaining market integrity and protecting investors from unfair market practices. These include:
- Take action against the misuse of confidential information for unfair gains.
- It protects investors by stopping unfair practices and providing ways to resolve complaints.
- Educate investors to understand risks by conducting awareness programs regularly.
2. Regulatory Functions
SEBI regulates all financial institutions and ensures proper market management through explicit rules and supervision. SEBI implements:
- Registrations for brokers, sub brokers, intermediaries and other market participants to ensure compliance with regulations.
- Regulations for mutual funds and portfolio managers set guidelines to protect investors' interests.
- Laying down rules for companies that issue shares to the public.
- Rules for monitoring and takeover of companies, ensuring corporate actions are conducted fairly and transparently.
3. Developmental Functions
Apart from regulating and monitoring, SEBI also plays a vital role in developing and modernizing the capital market. The efforts are being made as:
- Promoting investor education programs and encouraging financial awareness.
- Encouraging self regulatory organizations that support industry led initiatives for better governance.
- Introducing new financial instruments that facilitate innovation to meet ever changing market needs.
- Improving market infrastructure by upgrading systems, technology & processes to enhance efficiency.
Pro Tip: You can buy digital gold online while having the flexibility to trade anytime, anywhere.
In the next heading, let us find out the organizational structure of SEBI.
Start Your SIP TodayLet your money work for you with the best SIP plans.
The Organizational Structure and Governance of SEBI
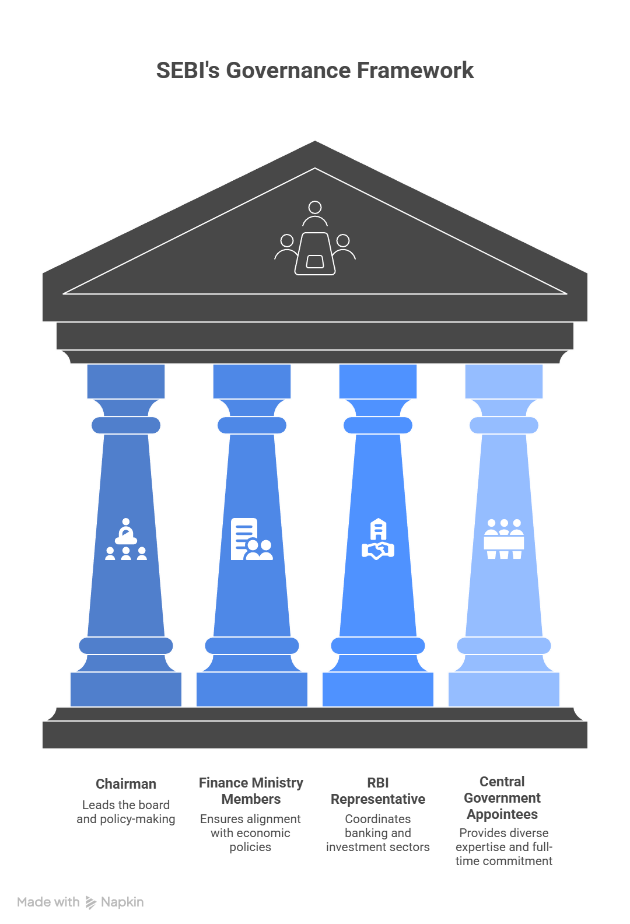
SEBI is run by a Board of Members who ensure that decision-making is balanced and transparent. The board is designed to include experts from various financial and legal sectors. The SEBI board consists of nine members and is organized as follows:
- The Chairman: The chairman leads the overall board and the policy-making of the regulator. The Central Government of India appointed him.
- Two Members: These officials are designated from the Union Finance Ministry to ensure alignment with the country's economic policies.
- One Member: The representative appointed from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to ensure coordination between the banking sector and the investment market.
- Five Other Members: These are appointed by the Central Government. At least three of whom must be Whole-Time Members who work exclusively for SEBI.
Also Read: Smart SIP Strategy to Build a ₹2 Crore Wealth in 2026
Let us know the other powers of SEBI in the Indian market.
What are the Powers of SEBI?
SEBI holds a unique and powerful position in the Indian financial system because it combines multiple types of authority to regulate the capital market effectively. The powers can be broadly described into:
-
Quasi-Judicial Powers
- Acts like a court to execute cases related to violations of securities law.
- Can pass orders against companies, brokers or individuals involved in unfair practices or activities.
- SEBI has the authority to impose penalties or suspend registrations.
-
Quasi-Executive Powers
- SEBI can investigate and inspect the market participants and intermediaries as and when necessary.
- It monitors trading activities to prevent fraudulent and scamming activities.
- Issues guidelines and takes corrective measures to establish discipline in the market.
-
Quasi-Legislative Powers
- SEBI Frames guidelines for brokers, mutual funds, IPOs and corporate governance.
- Set standards to ensure fairness and efficiency in the securities market.
- Design and develop the market framework to support long term growth and stability.
The SEBI, using its legislative powers, defines rules and guidelines which can be seen in the next section.
Key Rules and Guidelines of SEBI on Mutual Fund Investments
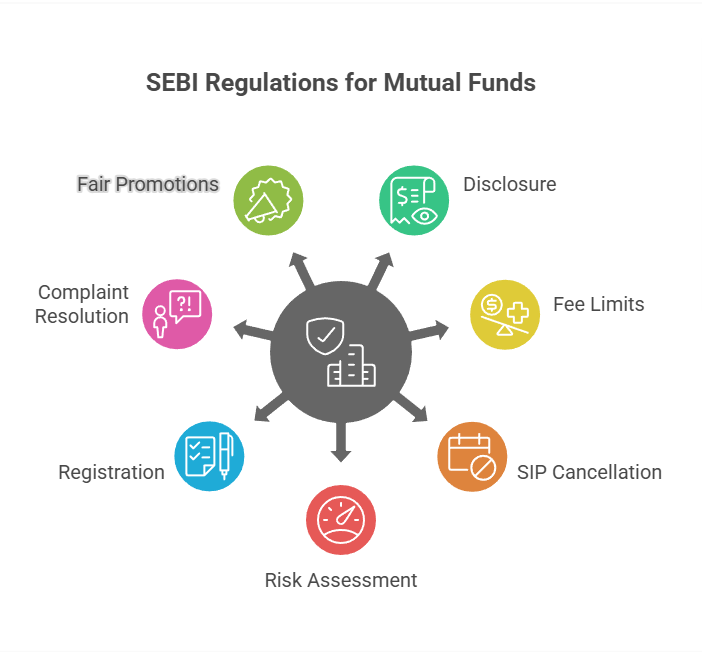
The SEBI has set several guidelines and frameworks to help make mutual funds safer, more reliable and investor friendly. The key regulations that guide mutual fund investments are discussed below:
- SEBI makes sure that mutual fund houses clearly disclose where your money will be invested, the risk involved and the cost or fees you will pay to avoid any hidden surprises.
- SEBI also decides the limit of fees charged by fund houses to protect your take-home money.
- SEBI also decides upon the fees so that your profits stay safe from high expenses and you get maximum returns from your investments.
- According to SEBI regulations, cancellation of a mutual fund SIPis permitted only after three consecutive instalments.
- Every mutual fund has to show its risk level using a simple risk-o-meter to analyze whether a fund matches your requirements.
- SEBI mandates the specific registrations of asset managers and trustees to reduce conflicts of interest and improve accountability.
- If an investor has any problem, SEBI provides an easy online system where investors can raise complaints and get them resolved efficiently.
- SEBI checks that the mutual fund promotions are fair enough to their commitments and that no fake commitments are made just to earn higher commissions.
Pro Tip: Use a SIP calculator to quickly calculate SIP returns on your mutual fund investments.
The above rules are just a glimpse of the power of SEBI and the role it plays in Indian markets.
Smart Investments, Bigger Returns
Conclusion
SEBI is the backbone of India’s financial market, which not only regulates the companies and other financial institutions but also provides a structured economic environment. This enables the Indian market to attract more and more investments through active investor participation.
The understanding of SEBI’s roles, functions and powers is essential for investors as it helps make them aware of potential risks in their mutual fund investments.
Related Blogs:
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How does SEBI deal with unregistered investment advisors?
SEBI takes strict action against unregistered advisors that includes penalties and trading bans to protect investors.
-
Does SEBI regulate cryptocurrency investments?
At present, cryptocurrencies do not fall under SEBI regulations, but certain crypto related products are monitored.
-
What happens if a broker violates SEBI rules?
SEBI can impose fines, suspend licenses or permanently ban brokers for serious violations.
-
Are SEBI rules applicable to foreign investors in India?
Yes, foreign investors must follow the rules of SEBI when investing in securities markets in India.
-
How does SEBI ensure cybersecurity in trading?|
SEBI mandates brokers and exchanges to follow strict cybersecurity and data protection measures.
-
Does SEBI regulate advertisements on social media?
Yes, SEBI has guidelines to prevent misleading financial promotions across digital and social media platforms.










.webp&w=3840&q=75)


