Table of Contents
- How to Plan Taxes for Salaried Employees?
- Understanding the Components of Your Income
- Understanding the Income Tax Slabs
- Deductions Under Section 80C
- Other Deductions and Exemptions for Salaried Individuals
- Standard Deduction
- Claiming House Rent Allowance (HRA)
- Claiming Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
- Capitalizing on NPS Contributions
- Tax Planning Tips for Salaried Employees
- Conclusion
Are you aware that nearly 70% of salaried individuals miss out on key deductions simply because they do not plan ahead? Effective income tax planning for salaried employees like you is a necessity in today’s financial world. With more tax saving options for salaried individuals than ever before, including Section 80C, HRA, NPS and standard deduction, tax planning has also become easier than ever before for you.
Imagine paying zero tax on incomes up to Rs 12.75 lakh simply by choosing the right tax regime and utilizing available deductions and exemptions. All you need to do is understand your salary structure and use tax saving schemes for effective tax planning for salaried employees.
This guide is packed with the best tax saving options for salaried individuals like you. So, explore the secrets to stress-free tax filing and discover how to retain more of your hard-earned money.
How to Plan Taxes for Salaried Employees?
As a salaried employee, it is crucial to know the factors related to the Income Tax applied to your salary for effective tax planning in India. The factors include determining your total income and its sources, the deductions & exemptions applicable to your Income and an investment strategy that will maximize your savings.
Consider the following points for doing an effective tax planning:
- Know your taxable Income and tax slabs.
- Claim all the deductions and exemptions that are available.
- Invest regularly and plan early for your taxes.
- Use employer benefits for tax savings.
- Keep good records, file them on time and seek professional advice.
Must Read: What is Tax Planning: Objectives, Types & Importance
Understanding the Components of Your Income
The salaries given to the individuals have various elements with different tax implications. Let us look at these elements in detail:
Key Salary Components
- Basic Salary:It is a fixed amount of money decided by both the employee and the employer, generally forming 40-50% of your total salary (CTC). This portion of your total Income is fully taxable.
- CTC (Cost to Company):It is the total expense the company incurs on an employee in a year.
Allowances
These are the additional benefits provided by the employer to cover various expenses incurred during the employment period. They are classified as:
| Taxable Allowance | Partially Taxable Allowance | Fully Exempted (Under the old regime) |
|---|---|---|
| Dearness Allowance (DA) | House Rent Allowance (HRA) | Daily Allowance |
| Entertainment Allowance | Leave Travel Allowance (LTA) | Traveling Allowance |
| Overtime Allowance | Conveyance Allowance | Mobile Reimbursement |
| City Compensatory Allowance (CCA) | Children Education Allowance | Books and Periodicals Reimbursement |
| Medical Allowance | Children Hostel Allowance | Food Coupons |
| Special Allowance | Medical Allowance | Relocation Allowance |
Perquisites (Perks)
These are the additional benefits provided to the employee, other than the salary, which include rent-free accommodation, car facility, club membership or gifts. Some of these are fully taxable and some may be exempt (depending on their nature and value).
Other Income
Other Income includes Income from house property (rental from a left-out property) and other sources (interest income from bank accounts or dividends).
Deductions
These are the amounts that are deducted from your total taxable income to reduce your overall tax liability. Some of them are:
| Deductions | Description |
|---|---|
| Standard Deduction | A deduction of Rs 50,000 for salaried individuals. |
| Professional Tax | A state-specific tax levied on salaried employees, professionals, and freelancers. |
| PF (Provident Fund) | Contributions to the Employee Provident Fund (EPF). |
| TDS (Income Taxes Deducted at Source) | Deducted tax from your salary by your employer and deposited by the government. |
| Other Deductions | Life or medical insurance premiums, contributions to NPS, interest on home & education loans, donations, etc. |
Now, let us learn about your income level and the rate of tax you need to pay based on your level through the Income Tax Slabs.
Understanding the Income Tax Slabs
In the Indian Tax System, the income tax slabs are used to determine the tax rate for an individual according to their income level.
There are two tax regimes in India- The Old Regime and the New Regime.
Income Tax Slab For FY 2024-25 (AY 2025-26)
-
New Tax Regime
| Income Level (Rs) | Income Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to 3,00,000 | Nil |
| 3,00,001 - 7,00,000 | 5% |
| 7,00,001 - 10,00,000 | 10% |
| 10,00,001 - 12,00,000 | 15% |
| 12,00,001 - 15,00,000 | 20% |
| Above 15,00,000 | 30% |
-
Old Tax Regime
| Income Level (Rs) | Income Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| For those below 60 years | |
| Up to 2,50,000 | Nil |
| 2,50,001 - 5,00,000 | 5% |
| 5,00,001 - 10,00,000 | 20% |
| Above 10,00,000 | 30% |
| For the age of 60-80 years | |
| Up to 3,00,000 | Nil |
| 3,00,001 - 5,00,000 | 5% |
| 5,00,001 - 10,00,000 | 20% |
| Above 10,00,000 | 30% |
| For those aged above 80 years | |
| Up to 5,00,000 | Nil |
| 5,00,001 - 10,00,000 | 20% |
| Above 10,00,000 | 30% |
-
Income Tax Slab Under New Regime For FY 2025-26 (AY 2026-27)
| Income Level (Rs) | Income Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to 4,00,000 | Nil |
| 4,00,001 - 8,00,000 | 5% |
| 8,00,001 - 12,00,000 | 10% |
| 12,00,001 - 16,00,000 | 15% |
| 16,00,001 - 20,00,000 | 20% |
| 20,00,001 - 24,00,000 | 25% |
| Above 24,00,000 | 30% |
Pro Tip: Use a Tax Calculator to help you estimate your income tax liability.
Deductions Under Section 80C
Here is how to properly utilize several tax-saving options for salaried professionals under Section 80C:
Limit and Eligibility
- Only individuals & HUFs are allowed to claim these deductions.
- It provides the deduction of Rs 1.5 lakh per year (maximum).
Eligible Investments and Expenses
It provides a range of qualified deductions, some of which are:
- PPF (Public Provident Fund): It is a tax-saving scheme backed by the government with tax-exempt interest used for long-term investments.
- NSC (National Savings Certificate): It is a fixed-income investment instrument that guarantees returns.
- ELSS (Equity-Linked Saving Schemes): It is a type of equity mutual fund with high return potential, but it has a 3-year lock-in period.
- EPF (Employee Provident Fund): It is a contribution to savings from your monthly salary used for retirement.
- SSY (Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana): It is a savings scheme that provides benefits for a girl child.
- Tax-Saving FDs (Fixed Deposits): They give guaranteed interest rates and have a lock-in period of 5 years.
Make a Strategy for Maximum Benefits
- Begin your tax planningearly to take advantage of compounding.
- Consider long-term investments and diversify by making investments in a variety of industries (Start SIPfor better investment).
- Make the most of your tax savings by taking advantage of the Rs 1.5 lakh full deduction limit.
Documentation and Filing
- As evidence, keep all of your records and investment documentation.
- Give this documentation to the employer for accurate TDS calculation.
- After filing your income tax return (ITR) and claiming deductions under Chapter VI-A, make sure your ITR is accurate.
Pro Tip: Use a SIP Calculator to estimate the future value of your monthly investments in mutual funds.
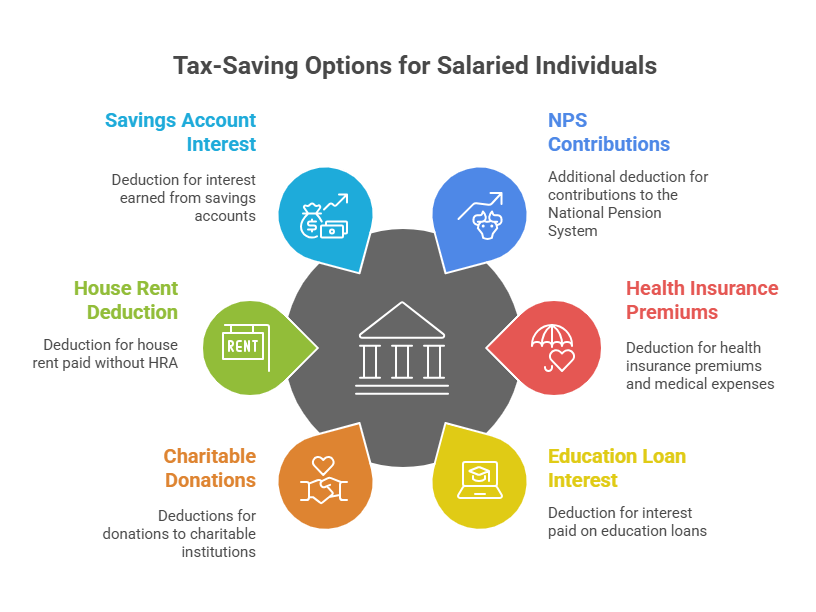
Other Deductions and Exemptions for Salaried Individuals
Some deductions and exemptions in tax-saving options for salaried individuals other than Section 80C under Chapter VI-A are:
- Section 80CCD(1B): Allows an additional deduction of Rs 50,000 for the contributions made to NPS (National Pension System).
- Section 80D: Provides a deduction for health insurance premiums and medical expenses.
- Section 80E: Allows deduction of the entire interest paid on an education loan.
- Section 80G: Provides deductions on donations made to certain funds and charitable institutions.
- Section 80GG: Deduction for house rent paid for individuals who did not receive HRA.
- Section 80TTA: Allows Rs 10,000 deduction on interest earned from a savings account.
Now, let us explore some tax-saving options for salaried individuals in the next part.
Also Read: How To Calculate Income Tax On Salary
Standard Deduction
Standard Deduction is one of the tax saving options for salaried employees and pensioners. It is crucial for tax planning as it provides a simple way of reducing your taxes. It is a fixed amount of money from your salary that is used as taxable Income when you pay taxes.
Significance in Tax Planning:
- It lowers your tax obligation, saving you money.
- It makes tax filing easier by eliminating the need to keep records.
- Because of its fixed nature, income tax planning is predictable.
- Regardless of income level, it applies to all eligible pensioners & salaried individuals.
Applicability & Amounts of Standard Deduction for FY 2024-2025 (AY 2025-26):
- Old Regime:Rs 50,000 deduction for salaried individuals.
- New Regime:Increased to Rs 75,000 for salaried individuals.
- Family Pensioners:Increased to Rs 25,000 from Rs 15,000.
Next, you will explore the details of how to claim HRA in India for the financial year 2025.
Claiming House Rent Allowance (HRA)
Here is how to claim HRA exemptions as tax-saving options for salaried employees in India for FY 2025-26:
Eligibility Criteria
- You must be a salaried employee and HRA must be a part of your salary.
- You must be living in a rented house and should be paying rent.
- HRA exemption is only available if you choose the old tax regime.
- Self-employed individuals can not claim HRA.
How much HRA can you claim?
The lowest of the following three amounts is how much HRA you can claim:
- Actual HRA received.
- Actual rent paid minus 10% of your salary.
- 50% of your salary (Basic Salary + DA) for metro cities or 40% for non-metro cities.
Documents Required for claiming an HRA exemption
- Rent receipts or a signed rental agreement.
- Landlord's PAN (if rent exceeds Rs 1 lakh annually).
- Bank or UPI statements.
- Salary slip/Form 16 reflecting HRA.
Process of claiming HRA
If claimed via the employer:
- Submit rent receipts, agreement and landlord's PAN (if required) to the employer before the end of the year.
- The employer will adjust your TDS according to the provided documents.
If not claimed via the employer:
- You can claim HRA directly when filing ITR under the old regime.
- There is a new section of HRA in the ITR form for FY 2024-25 (AY 2025-26). Fill in the mentioned information over there:
- Basic salary plus DA
- HRA received
- Rent paid
- City (metro or non-metro)
- Maintain all your required documents for verification by the Income Tax Department (if necessary).
Due Date: The last date to file your ITR and claim HRA exemption for FY 2024-25 (AY 2025-26) is September 15, 2025.

After HRA, let us learn the process and criteria to claim LTA in India.
Claiming Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
Here is how to claim LTA exemptions as tax-saving options for salaried employees in India for FY 2025-26:
Eligibility Criteria
- Available only under the old tax regime.
- LTA must be a part of your salary or CTC.
- Can be claimed twice in a set of 4 years.
- LTA only applies if you travel during the permitted leaves.
How much LTA can you claim?
LTA Exemption is limited to actual travel expenses incurred for the shortest route.
Documents Required for claiming an LTA exemption:
- Original tickets, boarding passes, and/or e-tickets (air/rail/bus).
- Invoices or bills from authorized travel operators.
- Proof of payment (bank/card/UPI statement).
- Filled LTA application and Form 12BB (if asked).
- Leave approval proof (may be required for scrutiny).
Process of claiming LTA
If claimed via the employer:
- Plan your trip and save all your original documents as proof.
- Apply for sanctioned leave and travel.
- Fill and submit the employer's LTA claim form.
- Submit documentation by the employer’s deadline (often March 31).
If not claimed via the employer:
You can claim the LTA exemption directly when filing your ITR under the old regime.
Due Date: Give all proofs to your employer by March 31 of the financial year.
Now, let us dive into another tax saving option for salaried employees.
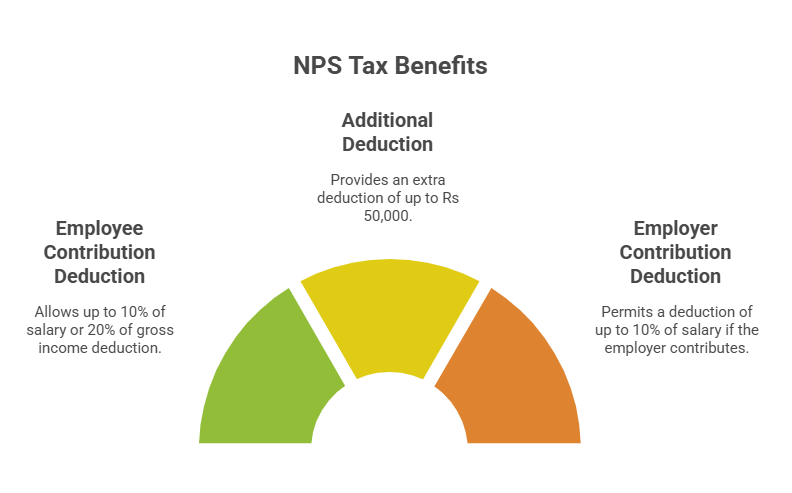
Capitalizing on NPS Contributions
NPS (National Pension System) contributions are a great option for planning your retirement, as it is a government-backed scheme for saving taxes. Tax benefits provided by NPS are:
- Section 80CCD(1): On the employee's contribution, a deduction of up to 10% of salary or 20% of gross income is allowed for self-employed individuals.
- Section 80CCD(1B): An additional deduction of up to Rs 50,000.
- Section 80CCD(2): Deduction up to 10% of salary if an employer contributes to NPS.
Now you must be wondering, “ How do you do effective tax planning?” Well, keep reading to learn some vital tax planning tips.
Essential Read: Top 10 Highest Taxpayers in India 2025: Who Pays the Most?
Tax Planning Tips for Salaried Employees
The following are the tips for a salaried individual for efficient tax planning:
- Understand tax slabs and salary structure to estimate your tax liability.
- Maximize by investing in instruments eligible for Section 80C deductions.
- Claim HRA (House Rent Allowance) exemptions.
- Claim health insurance premiums and medical expenses.
- Make good use of the NPS (National Pension System).
- Maximize home loan benefits.
- Claim the benefits from standard deductions.
- Explore other allowances and reimbursements.
- Decide between the old and new tax regimes carefully.
- File your Income Tax Returns (ITRs) timely.
Conclusion
In short, if you are a salaried individual and want to plan your taxes effectively in FY 2025-26, you need to grab every available deduction and exemption that can reduce your overall tax liability.
By understanding your salary structure, using available tax saving options for salaried professionals like Section 80C, HRA, LTA and NPS, you can transform your financial journey and do real savings.
Tax planning is all about making informed decisions, staying updated and filing your ITRs on time to avoid any penalties. Just be consistent and you can reduce your tax liability.
Related Blogs:
- What Is the Assessment Year in Income Tax?
- What is Professional Tax in Salary? Learn Tax Slabs, Deductions
FAQs
-
Which Saving Schemes Are The Best To Invest In?
The best options are PPF, ELSS, NPS and EPF because of their long-term growth, safety and tax advantages.
-
How Can Personal Loans Help You Achieve Financial Independence?
Personal loans provide quick cash for emergencies with proper management and independence.
-
How Are Personal Loan Apps Leading To A Financially Healthy India?
Loan apps encourage financial knowledge and better money management practices throughout India.
-
How to Set Personal Finance Goals?
First, compare your income and expenses and then determine specific, attainable goals and due dates for debt, investments and savings.
-
How to Set S.M.A.R.T. Financial Goals?
S.M.A.R.T. goals are time-bound, relevant, specific, measurable and achievable and guarantee practical financial planning and advancement.







.png&w=3840&q=75)
.webp&w=3840&q=75)


