Table of Contents
From using UPI to pay a chaiwala for your morning tea to getting loans for your startup to pursue big dreams, all of this is made possible by India's strong banking system, under the regulations of the RBI (Reserve Bank of India). But, did you know that the banking system of India carries different types of banks for different requirements?
Yes, there are many types of banks in India that serve the needs of all kinds of people, from the wealthy to farmers in villages, making the basic banking services accessible to everyone.
Now, you must be curious to know how many types of banks there are in India. Right? This post unlocks all the key information for you. And, that is not all, you will also get the lists of the top banks, along with the suggestions for choosing the right one that fits your life in 2026. So, skip the waiting and jump in to boost your financial game.
Buy Digital Gold Online Safely and Start Your Gold Journey at Just ₹100 now
Overview of the Banking System in India: What is Its Role in the Economy?
The Indian Banking System is a strong and flexible financial architecture that serves as the backbone of the national economy. It is regulated by the RBI (Reserve Bank of India), which includes various banks and financial institutions, all working together to support economic growth and fulfill commercial, rural and developmental needs.
Here are the primary roles of the banking sector in economic growth and stability:
- Banks give a safe space to people to save their money and turn it into productive investments.
- They act as the primary source of credit and capital formation.
- It supports financial inclusion, as it have bought many people into the formal banking system, promoting growth.
- Banks make it easy to transfer money and complete digital transactions.
- It brings financial stability to the country's economy.
Now, let us look at the types of banks that are working in India.
Types of Banks in India
The banking system in India includes different types of banks. These banks are mainly divided into two groups: Scheduled Banks and Non-Scheduled Banks.
Most of the banks that operate in India are Scheduled Commercial Banks, which are further divided based on their ownership and functions. The following are the main types of banks in India:
| Type of Bank | Ownership / Regulation | Primary Customers | Est. Year (Key Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central Bank | Govt of India | Govt, Commercial Banks | 1935 (RBI) |
| Public Sector Banks | Majority Govt-owned (>51%) | General Public, Businesses | 1955 (SBI) |
| Private Sector Banks | Private Shareholders | Urban Retail, Corporates | 1994 (ICICI) |
| Foreign Banks | Foreign Entities | NRIs, Corporates, HNIs | 1906 (Standard Chartered) |
| Cooperative Banks | Member-Owners | Local Communities, Farmers | 1910s (Urban Co-ops) |
| Small Finance Banks | Private (RBI licensed) | MSMEs, Unorganized Sector | 2016 (AU Small Finance) |
| Payments Banks | Private / Telecom (RBI) | Low-income, Migrants | 2016 (Airtel Payments) |
| Regional Rural Banks | Joint (Govt / PSB / Sponsor) | Rural Households, Agri-farmers | 1975 (Pragathi Gramin) |
| Local Area Banks (Rural) | Private (RBI limited area) | Specific Rural Districts | 1996 (Coastal LAB) |
| Specialized Banks | Govt / Statutory Bodies | Agri, Exports, Housing Sectors | 1982 (NABARD) |
Must Read: Top 10 Public Sector Banks in India 2026: Listed by Market Cap
After getting the list of the types of banks, let us uncover their services one by one in the next part.
Best Mutual Funds for 2026 Backed by Expert Research
Overview of the Types of Banks in India with the List of Top Banks
Here are the details of the types of banks operating in India. This section also contains the list of top banks in each category.
1. Central Bank
A central bank is the leading authority that manages a country's money. It controls the money supply, sets interest rates and ensures the stability of the financial system. These banks do not serve the public directly, they work with the government and other financial figures. The key services and functions of central banks are:
- It creates and implements monetary policy in India.
- They carry the power to issue national currency.
- They manage the bank accountsfor the government.
- These banks hold some cash reserves of the commercial banks, known as the Cash Reserve Ratio in India.
- They provide emergency loans to commercial banks during a financial crisis.
- These banks manage the foreign exchange reserves of India.
Examples of Central Banks
| Banks |
|---|
| The Reserve Bank of India |
| The US Federal Reserve |
| The European Central Bank |
2. Commercial Banks
They are the financial institutions that operate on a commercial basis. They accept deposits from the public and give out bank loans. It offers various financial services to individuals, businesses and governments. These are the primary services provided by the commercial banks:
- They provide savings accounts, current accounts and Fixed Deposits (FDs) and Recurring Deposits (RDs) to individuals.
- They provide personal and business loans.
- It helps with payments and transfers of both local and international trade.
The commercial banks are of three types, which are:
- Public Sector Banks: These banks are owned & operated by the government.
- Private Sector Banks:These are managed privately by individuals or organisations.
- Foreign Banks:The headquarters of these banks are located outside India, but they operate inside the country.
Examples of Commercial Banks
| Public Banks | Private Banks | Foreign Banks |
|---|---|---|
| State Bank of India | HDFC Bank | Standard Chartered Bank |
| Bank of Baroda | ICICI Bank | HSBC Ltd |
| Punjab National Bank | Axis Bank | Citibank N.A |
| Canara Bank | Kotak Mahindra Bank | Deutsche Bank |
| Union Bank of India | IndusInd Bank | DBS Bank India Limited |
3. Cooperative Banks
These banks are financial institutions that their members own and run. The members are also the customers. These banks focus on helping their community rather than just making a profit. Here are their primary services:
- These provide affordable bank loans & credit facilities at lower interest rates.
- They make basic banking services accessible for underserved communities and support rural development.
- These banks act as channels for implementing various government welfare and credit schemes in rural areas.
Examples of Cooperative Banks
| Cooperative Banks in India |
|---|
| Saraswat Co-operative Bank |
| Shamrao Vithal Co-operative Bank (SVC Bank) |
| Cosmos Co-operative Bank |
4. Small Finance Banks
SFBs are a type of bank that provides services to people who do not have access to basic banking services. The RBI approves it. They mainly serve small businesses, small and marginal farmers, micro and small industries and people working in the unorganized sector. The key services include:
- Provides basic banking services like savings accounts, current accounts and term deposits like FDs and RDs.
- Offers the service of lending, focusing on small loans.
- SFBs provide payment and money transfer services.
- They can also provide other financial products, such as distributing insurance and investment products like mutual fundsand pension schemes.
Examples of Small Finance Banks are-
| Banks |
|---|
| AU Small Finance Bank |
| Equitas Small Finance Bank |
| Ujjivan Small Finance Bank |
| Suryoday Small Finance Bank |
| Fincare Small Finance Bank |
5. Payments Banks
Their main goal is to help people who do not have access to banking services, like migrant workers, low-income families and small businesses. These banks work on a smaller scale than regular banks. Key services offered by payments banks are:
- You can have a demand deposit with a maximum balance of Rs 2,00,000 for each customer.
- They offer the facility of both domestic & international money transfers.
- They are allowed to issue ATM and debit cards, but cannot issue credit cards.
- With RBI approval, they can assist other banks by distributing financial products like mutual funds, insurance and pension plans, without sharing risks.
- They often work with existing services like post offices or telecom stores.
Examples of Payments Banks
| PBs in India |
|---|
| Airtel Payments Bank Ltd |
| Paytm Payments Bank Ltd |
| India Post Payments Bank Ltd |
| Jio Payments Bank Ltd |
| FINO Payments Bank Ltd |
| NSDL Payments Bank Ltd |
Pro Tip: Use a Mutual Fund Screener to filter and compare mutual funds for investments.
6. Rural Banks
In India, rural banks can be categorized into two basic categories:
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
These are specialized government-sponsored banks established under the Regional Rural Banks Act, 1976, to provide comprehensive banking and credit facilities in rural and semi-urban areas.
Examples of RRBs:
| Banks |
|---|
| Baroda Gujarat Gramin Bank |
| Uttar Bihar Gramin Bank |
| Saptagiri Grameena Bank |
Local Area Banks (LABs)
These are a smaller category of private banks introduced by the RBI in 1996 to mobilize rural savings and make them available for local investment. They work in a specific, limited area. They are set up in the private sector as joint stock companies.
Examples of LABs
| Banks |
|---|
| Coastal Local Area Bank Ltd. (Andhra Pradesh) |
| Kerala District Central Cooperative Bank |
7. Specialized Banks
These are also known as DFIs (Development Financial Institutions), which focus on specific areas of the economy to help businesses grow. They provide long-term funding for projects that traditional banks may avoid because of higher risks or longer time frames for getting returns. The following are the primary services provided by these banks:
- These banks offer industrial finance for manufacturing setups
- Offers export-import finance, including credit guarantees and trade loans
- Provides development finance and housing finance services.
- Give an infrastructure finance service that supports roads, power and ports.
Examples of Specialized Banks
| Banks |
|---|
| National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) |
| Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) |
| Export-Import Bank of India (EXIM Bank) |
| National Housing Bank (NHB) |
Pro Tip: Use a SIP Calculator and estimate the future returns of your SIP investment easily.
In the next heading, you will learn how to choose a good bank for yourself that will boost your financial stability. So, stay tuned.
Also Read: Top 10 Private Banks in India: Performance and their Overview
Start Your SIP TodayLet your money work for you with the best SIP plans.
How to Choose the Right Bank for Yourself in India?
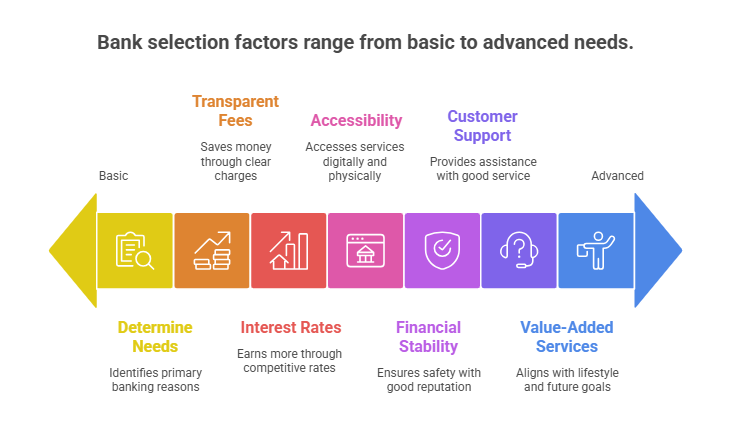
Choosing the correct type of bank in India depends on your financial needs & lifestyle choices. The following are the factors to consider to choose a right bank in India:
- Step 1: Determine your primary reasons for banking. Your needs will decide which type of bank and account is best for you.
- Step 2: Select a bank with a transparent fee structure to help you save more.
- Step 3: If your goal is to earn interest, then compare the interest rates given by different banks before picking a bank.
- Step 4: Consider both digital and physical accessibility of the bank.
- Step 5: Choose a financially stable bank with a good reputation and SEBI registration.
- Step 6: Go for a bank that has good customer support.
- Step 7: Look for value-added services that align with your lifestyle & future goals.
Lastly, let us learn the regulations that are imposed on the banks in India for safety purposes.
Pro Tip: Use a SWP Calculator to plan for your regular mutual fund unit withdrawals.
Banking Regulations in India
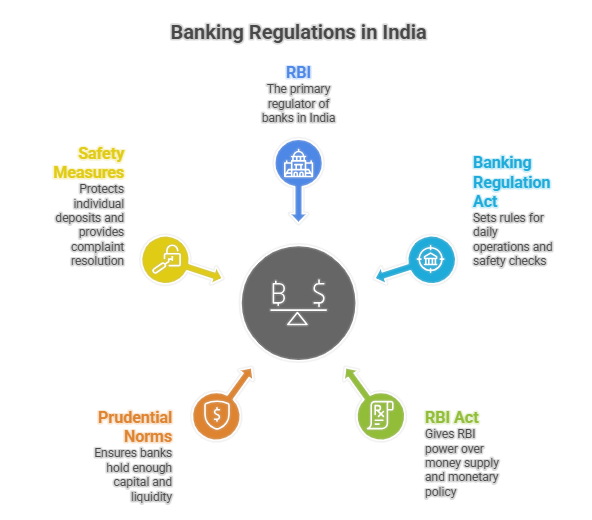
RBI is the primary regulator of banks in India, handing out licenses, keeping tabs on commercial and cooperative banks and maintaining a good financial system.
Main Laws for the Banking System in India
- Banking Regulation Act, 1949: This sets rules for daily operations & safety checks.
- RBI Act, 1934: It gives the RBI power over money supply, managing currency and controlling monetary policy. It acts as the government's banker.
Prudential Norms of Banks
- Capital Rules: According to this rule, banks must hold enough cash cushions (Basel III style) to handle loan defaults or shocks.
- Liquidity Buffers: The buffers, like CRR (Cash reserves with RBI) & SLR (government bonds), ensure banks would not run out of money during crises.
- Risk Controls: There are clear rules that apply to bank loans, markets, cyber threats and real-time fraud alerts.
Safety Measures for Individuals
- The DICGC protects your deposits up to Rs 5 lakh for each account, so your money is safe, even if a bank fails.
- The Ombudsman Scheme provides quick & free solutions for complaints, so you do not have to go to court.
Pro Tip: Use a Step-up SIP calculator to estimate your growing investments for faster wealth growth.
Conclusion
In short, India's banking system supports everything from small farms to city startups. It combines strong oversight from the RBI with different options that suit people’s needs.
You can trust big banks like SBI for their broad reach, or choose private banks like HDFC for their fast mobile apps. There are also niche banks like NABARD that focus on rural development. Make wise choices by comparing fees, interest rates and digital access in 2026.
Related Blogs:
- Buy Now Pay Later Explained (2026) – Benefits & Hidden Risks
- Best Way to Save Money: Expert Tips to Grow Wealth Faster
FAQs
-
What is new in banking rules for 2026?
In 2026, the RBI is promoting digital KYC, closing dormant accounts and updating Basel III standards.
-
What makes public sector banks different from private ones?
Public banks offer government-backed programs. Private banks are known for their attractive apps, quicker loan approvals and higher interest rates on FDs.
-
Can I switch banks easily in 2026?
Yes, the RBI's Account Aggregator allows you to easily transfer UPI, loans and fixed deposits without any complicated paperwork within 3 days.
-
Does deposit insurance cover all banks?
Yes, the DICGC protects up to Rs 5 lakhs for each person across all savings accounts, fixed deposits and recurring deposits at each bank.
-
What if my bank account goes dormant?
If there has been no activity in your account for 2 years, you need to take action. The RBI's new rule requires you to notify them via the app or at a branch to keep your account active.







.webp&w=3840&q=75)




